A hungry man weighing take quickly lunch, and then climbs up a mountain making it to a height of . If of food energy was wasted as heat and the rest was used as climbing work. The fuel intake could have been any one of the following with given enthalpy of combustion?

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Thermodynamics from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
1. Thermodynamics:
The study of energy changes between system and surrounding is called thermodynamics. There are three types of systems, such as open, closed and isolated.
2. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics:
If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third one, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
3. First Law of Thermodynamics:
Heat supplied to a system is equal to algebraic sum of the change in internal energy of the system and mechanical work done by the system.
(i)
(ii) Sign convention:
(a) Heat absorbed by the system positive
(b) Heat rejected by the system negative
(c) Increase in internal energy (i.e., rise in temperature) positive
(d) Decrease in internal energy (i.e., fall in temperature) negative
(e) Work done by the system positive
(f) Work done on the system negative
(iii) For isochoric process:
(a) In this process, constant.
(b)
(c)
(d)
(iv) For isobaric process:
(a) In this process, constant.
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(v) For adiabatic process:
(a) In this process,
(b) constant.
(c) constant.
(d) constant.
(e)
(vi) For isothermal process:
(a) In this process, constant or
(b) constant.
(c)
(d)
(vii) For any general polytropic process:
(a) constant
(b) Molar heat capacity,
(c) Work done by gas,
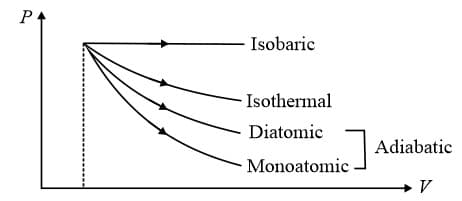
(d) Slope of diagram (also known as indicator diagram) at any point is
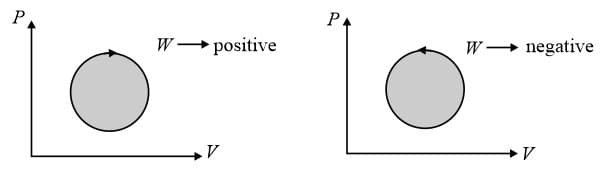
(viii) For cyclic process,
(a)
(b)
4. Second Law of Thermodynamics:
(i) Kelvin–Planck statement:
It is impossible to construct an engine operating in a cycle that will produce no effect other than extracting heat from a reservoir and performing an equivalent amount of work.
(ii) Rudolph Clausius statement:
It is impossible to make heat flow from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature without doing external work on the working substance.
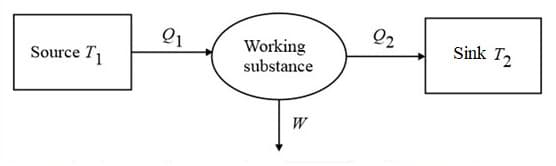
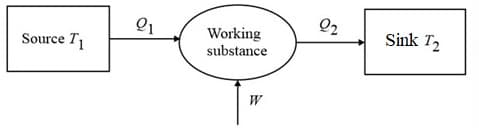
5. Heat Engines and Refrigerators:
(i) Carnot engine: It is a hypothetical engine with maximum possible efficiency.
Process are isothermal.
Process are adiabatic.
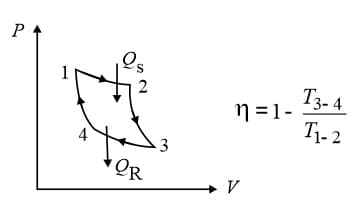
(ii) Efficiency of a cycle:
(a) For Carnot cycle:
(b) For refrigerator:
Coefficient of performance,
6. Bulk Modulus of Gases:
(i)
(ii) Isothermal bulk modulus of elasticity, .
(iii) Adiabatic bulk modulus of elasticity, .
7. Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams:
(i) Work done is least for monoatomic gas (adiabatic process).
(ii) Air quickly leaking out of a balloon becomes cooler as the leaking air undergoes adiabatic expansion.
(iii) First law of thermodynamics does not forbid the flow of heat from the lower temperature to the higher temperature.
(iv) First law of thermodynamics allows many processes which actually do not happen.