A length of copper track on a printed circuit board has a cross-sectional area of The current in the track is . You are provided with some useful information about copper:
of copper has a mass of
of copper contains atoms In copper, there is roughly one electron liberated from each copper atom
(a) Show that the electron number density for copper is about .
of copper has a mass of

Important Questions on Electric Current, Potential Difference and Resistance
A length of copper track on a printed circuit board has a cross-sectional area of The current in the track is . You are provided with some useful information about copper:
of copper has a mass of
of copper contains atoms In copper, there is roughly one electron liberated from each copper atom
(b) Calculate the mean drift velocity of the electrons.
(a) Explain the difference between potential difference and e.m.f.
(b) A battery has negligible internal resistance, an e.m.f. of and a capacity of (ampere-hours). Calculate:
(i) The total charge that it can supply
(c) The battery is connected to a lamp. Calculate the resistance of the lamp.
Some electricity-generating companies use a unit called the kilowatt-hour to calculate energy bills. is the energy a kilowatt appliance transfers in hour.
(b) An electric shower heater is rated at .
(i) Calculate the current it will take from the mains supply.
Some electricity-generating companies use a unit called the kilowatt-hour to calculate energy bills. is the energy a kilowatt appliance transfers in hour.
(b) An electric shower heater is rated at .
(ii) Suggest why the shower requires a separate circuit from other appliances.
Some electricity-generating companies use a unit called the kilowatt-hour to calculate energy bills. is the energy a kilowatt appliance transfers in hour.
(b) An electric shower heater is rated at .
(iii) Suggest a suitable current rating for the fuse in this circuit.
A student is measuring the resistance per unit length of a resistance wire. He takes the following measurements.
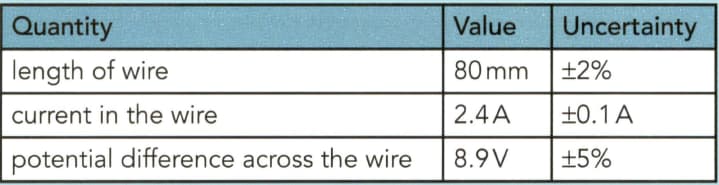
(a) Calculate the percentage uncertainty in the measurement of the current.
