A light ray is incident on a transparent sphere of index. at a angle of incidence. What is the deviation of a tiny fraction of the ray, which enters the sphere, undergoes two internal reflections and then refracts out into air?

Important Questions on Ray Optics
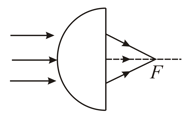
A paraxial beam is incident on a glass hemisphere of radius in air as shown. The distance of point of convergence form the plane surface of hemisphere is:
A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature , separates two medium and of and respectively. If the object placed along principal axis in medium , then:
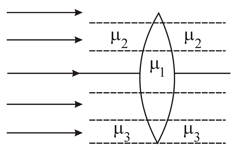
A double convex lens, made of a material of refractive index , is placed inside two liquids of refractive indices and , as shown. . A wide, parallel beam of light is incident on the lens from the left. The lens will given rise to:
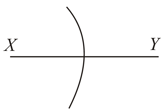
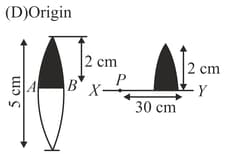
A converging lens of focal length and diameter is cut along the line . The part of the lens shown shaded in the diagram is now used to from an image of a point placed away from it on the line which is perpendicular to plane of the lens. The image of will be formed.
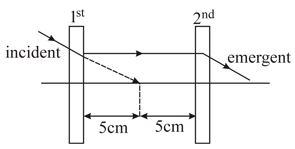
Look at the ray diagram shown, what will be the focal length of the and the lens, If the incident light ray passes without any deviation?
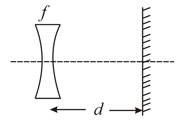
A diverging lens of focal length is placed in front og a plane mirror as shown in the figure. Light from a very far away source falls on the lens. The final image is at a distance: