A metal rod, of length expands by, when, its temperature is raised from to . Another rod, of a different metal of length expands by, for the same rise in temperature. A third rod, of length is made up of pieces of rods, and placed end to end, expands by on heating from to . Find the lengths of each portion of the composite rod.

Important Questions on Thermometry, Thermal Expansion and Calorimetry
A steel rail long is firmly attached to the roadbed only at its ends. The sun raises the temperature of the rail by , causing the rail to buckle. Assuming that the buckled rail consists of two straight parts meeting in the centre, calculate how much the centre of the rail rises. Coefficient of linear expansion of steel is .
A copper plate and a tungsten plate having a thickness each are riveted together so that at they form a flat bimetallic plate. Find the average radius of the curvature of this plate at temperature . The coefficients of linear expansion for copper and tungsten are and
The figure shows a rectangular plate of dimension from which two circular holes of radii and have been cut. The distance between the two holes is .
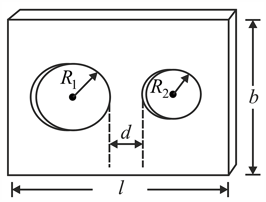
What happens to all these distances and dimensions when the plate is heated up?
The figure shows a rectangular plate of dimension from which two circular holes of radii and have been cut. The distance between the two holes is .
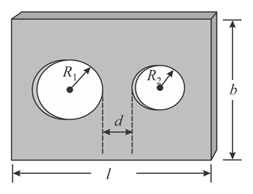
If and are the respective lengths at a higher temperature, then determine the relations between the ratios and .
A clock with a brass pendulum shaft keeps correct time at a certain temperature.
How closely must the temperature be controlled if the clock is not to gain or lose more than a day? Does the answer depend on the period of the pendulum?
A clock with a brass pendulum shaft keeps correct time at a certain temperature.
Will an increase of temperature cause the clock to gain or lose?
A pendulum clock loses a day if the temperature is and goes fast by a day if the temperature is . Find the temperature at which the clock will show correct time and the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal of the pendulum shaft.
