A monatomic ideal gas sample is given heat . One half of this heat is used as work done by the gas and rest is used for increasing its internal energy. The equation of process in terms of volume and temperature is
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
The equation of state of moles of a non-ideal gas can be approximated by the equation where, and, are constant characteristics of the gas. Which of the following can represent the equation of a quasi-static adiabatic for this gas (assume that, is the molar heat capacity at constant volume is independent of temperature)?
When a system is taken from state to state along the path , it is found that and . Along the path , . along the path is,
| Column – 1 | Column – 2 | Column – 3 |
| (I) | (i) Isothermal | (P) 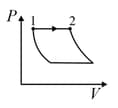 |
| (II) | (ii) Isochoric | (Q) 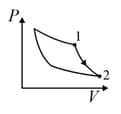 |
| (III) | (iii) Isobaric | (R) 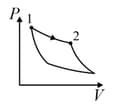 |
| (IV) | (iv) Adiabatic | (S) 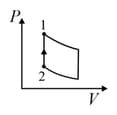 |
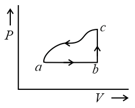
One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from to along a path as shown in figure. The change in internal energy of the gas during the transition is
(I) and
(II) and
(III) and
(IV) and
Which of the above will lead to an increase in the internal energy of the system?
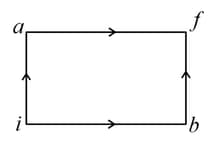
The diagram shown below indicates two paths along which a sample of gas can be taken from state to state . The energy equal to in the form of heat is required to be transferred if the Path- is chosen. How much energy in the form of heat should be transferred if Path- is chosen?
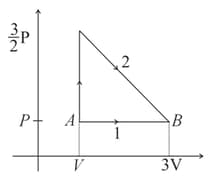
Match the thermodynamics processes taking place in a system with the correct conditions. In the table : is the heat supplied, is the work done and is change in internal energy of the system.
| Process | Condition | ||
| (I) | Adiabatic | (A) | |
| (II) | Isothermal | (B) | |
| (III) | Isochoric | (C) | |
| (IV) |
Isobaric |
(D) |
An air bubble rises from the bottom of a water tank of height . If the initial volume of the bubble is . What will be its volume as it reaches the surface. Assume that its temperature does not change.
[, density of water ]
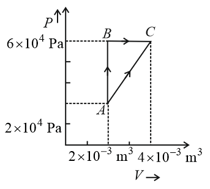
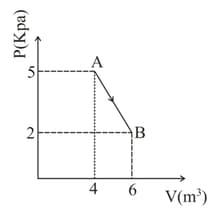
In process AB, of heat is added to the system and in process BC, of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be:

