MEDIUM
Earn 100
A non conducting solid cylinder of infinite length having uniform charge density and radius of cylinder is . Find the flux passing through the surface as shown in figure.
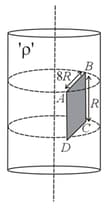

(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
46.15% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Electrostatics
HARD
for
for .
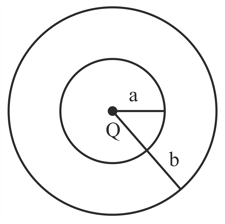
does not depend on x and y. If this potential is generated by a constant charge per unit volume (in units of ) which is spread over a certain region, then choose the correct statement.
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
EASY
EASY
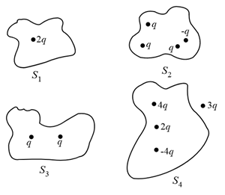
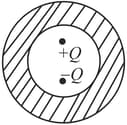
Let the respective electric fluxes through the surfaces be and . Then:
HARD
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
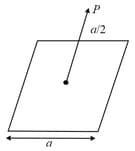
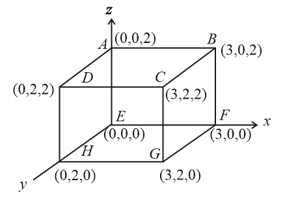
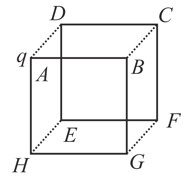
A point charge is placed at the corner of a cube of side as shown in the figure. What is the electric flux through the face ?
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY