A parallel plate air capacitor is charged to a certain potential difference. A dielectric plate is then inserted in the capacitor. In order to attain the initial potential difference, the charge on the plates has to be increased to three times. Determine the dielectric constant of the plate.

Important Questions on Capacitors and Dielectrics
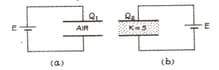
A parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance C, with air between the plates, is shown in Fig. (a).
A sheet of dielectric constant is introduced between the plates so as to fill the space, as shown in Fig. (b). What are the values of the potential differences and across the plates in case (a) and (b) respectively? What are the charges and on the plates? In both cases, a battery of emf is kept connected to the capacitor.
A, B, C and D are four ‘thin’, similar metallic parallel plates, equally separated by distance d and connected to a cell of PD V as shown.
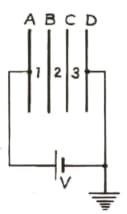
Write the potentials at A, B, C and D.
A, B, C and D are four ‘thin’, similar metallic parallel plates, equally separated by distance d and connected to a cell of PD V as shown.
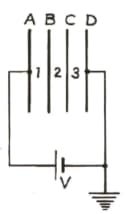
If B and C be connected by a wire, then what will be the potentials of the plates?
A, B, C and D are four ‘thin’, similar metallic parallel plates, equally separated by distance d and connected to a cell of PD V as shown.
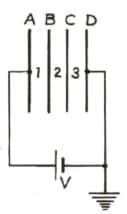
How will the electric fields change in the spacings between the plates ?
A, B, C and D are four ‘thin’, similar metallic parallel plates, equally separated by distance d and connected to a cell of PD V as shown.
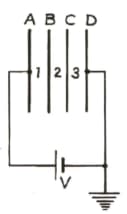
Will the charges on the plates A and D change?
A capacitor of capacitance C is charged up to a potential difference V. After removing the charging battery, the capacitor is connected in parallel with an uncharged capacitor of the same capacitance. What will be the effect on potential difference of first capacitor in this case.
