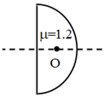
A plastic hemisphere has a radius of curvature of 8 cm and an index of refraction of 1.2. On the axis half way between the plane surface and the spherical one (4 cm from each) is a small object O. The distance between two images when viewed along the axis from the two sides of the hemisphere is approximately in cm.
Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
If the whole set up is immersed in water without disturbing the object and the screen positions, what will one observe on the screen?
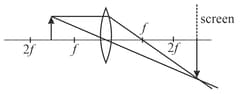
A small object is placed to the left of thin convex lens of focal length . A convex spherical mirror of radius of curvature is placed to the right of the lens at a distance of . The mirror is tilted such that the axis of the mirror is at an angle to the axis of the lens, as shown in the figure. If the origin of the coordinate system is taken to be at the centre of the lens, the coordinates (in ) of the point at which the image is formed are:
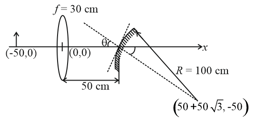
A light ray enters a solid glass sphere of refractive index at an angle of incidence . The ray is both reflected and refracted at the farther surface of the sphere. The angle (in degrees) between the reflected and refracted rays at this surface is:
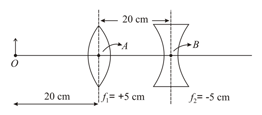
[ Assume both surfaces of the lens have same radius of curvature ]
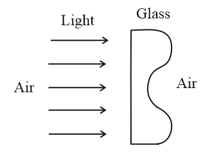
A parallel beam of light strikes a piece of transparent glass having cross section as shown in the figure below. Correct shape of the emergent wavefront will be (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)