A ray is incident on the plane surface of the glass slab (kept in air) of refractive index at an angle of incidence equal to the critical angle for this air-glass system. The refracted ray undergoes partial reflection and refraction at the other surface. The angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray at that surface is


Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
One face of a rectangular glass slab of the thickness is silvered. A point object is placed at in front of the unsilvered face and its image is formed behind the silvered face. If the refractive index of glass is then find the value of .
An air bubble is formed inside water. The refractive index of water is . At what distance from the air bubble should a point object be placed, so as to form a real image at the same distance from the bubble?
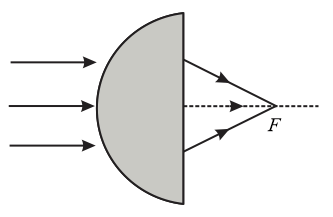
A paraxial beam is incident on a glass hemisphere of radius in air as shown. The distance of point of convergence from the plane surface of hemisphere is
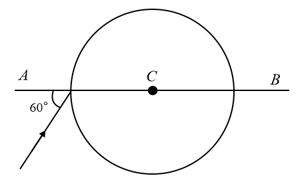
A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre at as shown in figure. The ray emerges from the sphere parallel to line . Find the refractive index of the sphere.
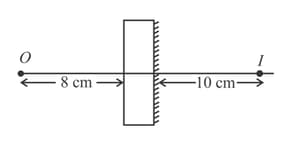
In the given figure, if object is placed at a distance of from , then find the image distance from •
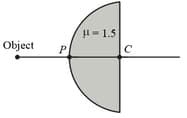
A point object is placed at a distance of from point on glass hemisphere of radius . If refractive index of hemisphere is , then position of its image from is
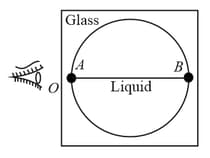
The observer sees the distance as infinitely large. If the refractive index of the liquid is and that of glass is , then is
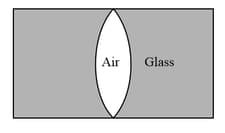
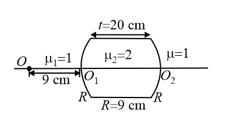
In the figure shown below, an air lens of radii of curvature is cut in a cylinder of glass . The focal length and the nature of the lens is