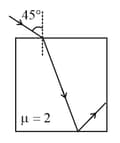
A ray is incident on the plane surface of the glass slab (kept in the air) of refractive index at an angle of incidence equal to the critical angle for this air-glass system. The refracted ray undergoes partial reflection and refraction at the other surface. The angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray at that surface is:


Important Questions on Ray Optics
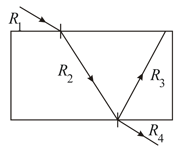
Bottom face of the glass cube is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incident on the top face of the cube a shown. Find the deviation of the ray when it comes out of the glass cube.
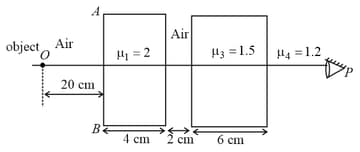
The distance of final image from as observed by observer is:
A ray of light is incident upon an air/water interface ( it passes from air into water) at an angle of . Which of the following quantities change as the light enter the water?
(I) wavelength
(II) frequency
(III) speed of propagation
(IV) direction of propagation
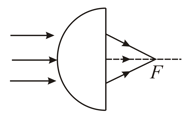
A paraxial beam is incident on a glass hemisphere of radius in air as shown. The distance of point of convergence form the plane surface of hemisphere is: