A small number of other animal species have opposable thumbs including the other great apes, gibbons, African and Asian monkeys, and also koalas. Discuss whether all animals with opposable thumbs should be classified together in one group.

Important Questions on Form
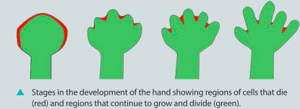
Human hands start to develop at an early stage of embryonic development. By day 32 of normal development, 8 mm long paddle-shaped hand plates have formed with no signs of a thumb or fingers. By day 52, there are separate digits and the hand is 23 mm long. Digit formation is accomplished by the programmed death of some cells and the growth and division of other cells. Sometimes babies are born with a deformity of the hands. Gene mutations can affect the development of digits. Polydactyly is having an extra finger or thumb. Syndactyly is the condition where two or more digits are fused together. Explain how polydactyly and syndactyly could develop in an embryo?
The drug thalidomide was used in some countries between 1957 and 1961 to treat nausea and morning sickness in pregnant women. Thalidomide caused abnormal development of the arms and hands in over 10,000 children whose mothers took the drug during pregnancy. In Germany, the sale of thalidomide was unrestricted. In the UK, it was available only with a prescription from a doctor. In the United States of America, the manufacturers of the drug repeatedly requested a license from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Each time the FDA refused a license until drug safety trials had been done on pregnant women, but the manufacturers repeatedly refused to do these trials. There was a view that a drug such as thalidomide could not cross the placenta and reach a developing fetus so, tests were unnecessary. The FDA refused a total of six requests for license and the number of children born with deformities due to thalidomide was far smaller than in Germany or the UK.
Explain the mistakes that were made that led to so many children being harmed by thalidomide in Germany and the UK.
Countless images of hands have been produced. Two are shown below: a drawing of praying hands by Albrecht Dürer and hands that are part of a sensory homunculus in which parts of the body are sized according to the area of cortex in the brain that receives sensory information from them. Discuss how well each of the two images helps us understand our identity.


