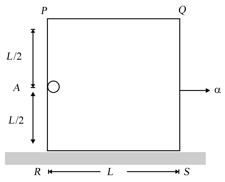
A small solid ball of density is held inside at point in a cubical container of side , filled with an ideal liquid of density as shown in the figure. Now, if the container starts moving with constant acceleration horizontally and the ball is released from point simultaneously, then choose the correct option(s).


Important Questions on Fluid Mechanics
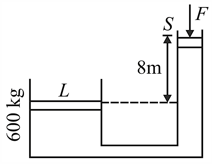
A vessel with a symmetrical hole in its bottom is fastened on a cart. The mass of the vessel and the cart is With what force (in should the cart be pulled so that the maximum amount of water remains in the vessel. The dimensions of the vessel are as shown in the figure. Given that area of base

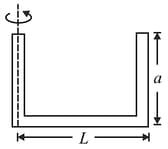
A solid cylinder of height and mass is floating in a liquid of density as shown in the figure. Find the acceleration of the vessel (in ) containing liquid for which the relative downward acceleration of the completely immersed cylinder w.r.t. vessel becomes equal to one-third of that of the vessel. (Take )

Find the value of
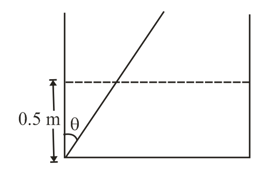
Length of a horizontal arm of a U-tube is and ends of both the vertical arms are open to atmospheric pressure A liquid of density is poured in the tube such that liquid just fills the horizontal part of the tube as shown in figure. Now one end of the open ends is sealed and the tube is then rotated about a vertical axis passing through the other vertical arm with angular speed If length of each vertical arm is and in the sealed end liquid rises to a height find pressure in the sealed tube during rotation. (in )
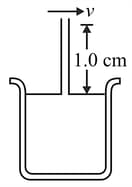
When air of density flows across the top of the tube shown in the accompanying figure, water rises in the tube to a height of . What is the speed of the air (in )?
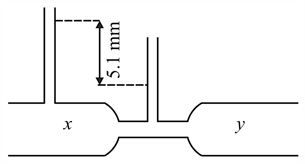
The diagram shows venturi meter through which water is flowing. The speed of water at is . Find the speed of water at in . (taking ).
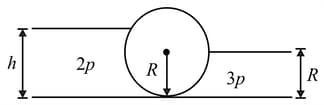
In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius, ) kept on a smooth surface separates two liquids of densities and . The height (in meter) for the translational equilibrium of the cylinder must be
For the system shown in the figure, the cylinder on the left at has a mass of and a cross sectional area of . The piston on the right, at , has cross sectional area and negligible weight. If the apparatus is filled with oil Find the force (in ) required to hold the system in equilibrium. Take .