A solution of is diluted to times of its initial volume. of this diluted solution requires of for complete oxidation. The volume strength of original solution is-

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Hydrogen from Embibe Experts Gamma Question Bank for Engineering Chemistry Solutions
1. Introduction:
Most abundant element of the universe, which was first prepared by Cavendish by the action of acids on certain metals. Its name hydrogen was proposed by Lavoisier because it produces water when burnt in oxygen. Hydrogen is the lightest element which is found in nature both in free state and in combined state.
2. Position of hydrogen in the Periodic Table:
The electronic configuration of hydrogen is , due to which it shows resemblance with alkali metals as well as halogens.
3. Resemblance with alkali metals:
(i) Its electronic configuration is like alkali metals.
(ii) It is a good reducing agent like alkali metals.
(iii) It can lose one electron to form ion like alkali metals.
(iv) It shows oxidation state like alkali metals when bonded to nonmetals.
4. Resemblance with halogens:
(i) It is a non-metal.
(ii) It forms a diatomic molecule.
(iii) It is gas like and
(iv) It can gain one electron to form ion.
(v) It is electronegative in nature.
(vi) Its ionization energy is high like halogens.
(vii) It is liberated at anode when is electrolysed.
(viii) It shows oxidation state when bonded to metal.
(ix) It forms many covalent compounds like halogens.
(x) On the basis of its marked resemblance with alkali metals and halogens, it is very difficult to place it either with the elements of group- or those of group-.
5. Isotopes of hydrogen:
Hydrogen has three isotopes.
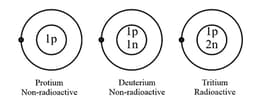
Physical properties of isotopes are different whereas their chemical properties are same.
6. Physical properties:
Important physical properties of hydrogen are as follows:
(i) It is colorless, odorless, tasteless gas.
(ii) Dihydrogen has two nuclear spin isomers called ortho and para-dihydrogen.
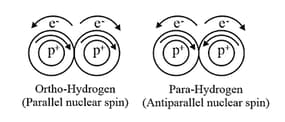
Atmosphere contains ortho- and para , Ortho- and Para- have and nuclear spin, respectively. With the decrease in temperature percentage of para-form increases and it can be up to .
7. Hard Water and Soft Water:
Depending upon the behavior of water towards soap solution. Water may be classified as soft and hard water.
The hardness of water may be:
Temporary hardness - due to presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium.
Permanent hardness - due to sulphates or chloride of calcium and magnesium.
Removal of Hardness: Temporary hardness of water can be removed by following methods:
(i) By boiling:
(ii) By Clark's process:
Permanent hardness can be removed by any of the following method:
(iii) Washing Soda treatment: It converts soluble calcium and magnesium compounds into insoluble carbonates.
(iv) Permutit: The sodium ions of permutit are exchanged with calcium and magnesium ions when hard water is passed through it.
, permutit can be regenerated by treatment of brine solution.
(v) Calgon: Calcium and magnesium salts present in hard water react with calgon to give complex salt.
(vi) Ion exchange resins: lon exchange resins are giant organic molecule of high molecular masses which are of two types:
(a) Cation exchanger [e.g., ]
(b) Anion exchanger [e.g., ]
8. Hydrogen Peroxide:
Hydrogen Peroxide
is with half open book like structure with polar bond and non-polar bond.
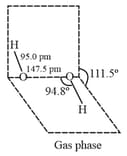
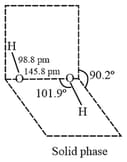
(i) Preparation: is prepared by the following methods:
(a) By action of acid on peroxides:
(b) By electrolysis of or
At Cathode: -
At Anode:
(c) By catalytic reduction of -ethyl (or butyl) anthraquinone to corresponding quinol and oxidising the latter with oxygen.
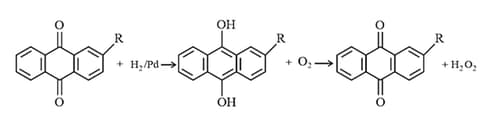
(iii) Chemical Properties:
(a) Oxidizing property: Hydrogen peroxide acts as an oxidizing agent both in acidic as well as in alkaline medium.
In acidic medium
(slow)
In basic medium
(fast)
(b) Reducing Property: In presence of strong oxidizing agents, hydrogen peroxide behaves as a reducing agent in both the medium.
Acidic Medium:
Alkaline medium:
(c) Acidic property: is a weak acid . It has two ionisable atoms. It forms two series of salts.
(d) Decomposition: is an unstable liquid
9. Volume strength of :
Volume strength of , solution is defined as volumes of evolved at in that is obtained per of solution after complete decomposition i.e., if litre solution of gives liters of oxygen at volume strength of is 10 volumes.
Volume strength of or
Reaction: -
