A survey was made of the Bengal dayflower Commelina benghalensis, growing on a lawn and in a field of young soybean plants. Ten 1.0 m2 quadrats were placed randomly in each area and the number of dayflower plants in each quadrat was counted. The results are shown in the given table:
Ouadrat
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Number od dayflowers on lawn
0
0
4
3
0
1
2
4
0
3
Number of dayflowers in field
0
0
0
2
5
0
0
1
0
0
Calculate the species frequency and species density of dayflower plants in each of the two areas.

Important Questions on Classification Biodiversity and Conversation
A survey was made of the Bengal dayflower Commelina benghalensis, growing on a lawn and in a field of young soybean plants. Ten 1.0 m2 quadrats were placed randomly in each area and the number of dayflower plants in each quadrat was counted. The results are shown in the given table: Calculate the species frequency and species density of dayflower plants in each of the two areas.
| Ouadrat | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Number of dayflowers on lawn | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| Number of daylfowers in field | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Explain why it is important to use randomly placed quadrats for this survey?
A survey was made of the Bengal dayflower Commelina benghalensis, growing on a lawn and in a field of young soybean plants. Ten 1.0 m2 quadrats were placed randomly in each area and the number of dayflower plants in each quadrat was counted. The results are shown in the given table:
| Ouadrat | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Number of dayflowers on lawn | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| Number of daylfowers in field | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Suggest two disadvantages with calculating percentage cover or using an abundance scale such as The Braun-Blanquet scale.
A sample was made of the animals on two rocky shores. Ten Quadrats were placed on each shore, and the number of animals of each species in each quadrat was counted.
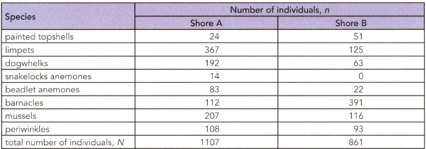
Calculate the D (Simpson’s Diversity Index) for Shore B by using the results given in the table.
A sample was made of the animals on two rocky shores. Ten Quadrants were placed on each shore, and the number of animals of each species in each quadrant was counted.
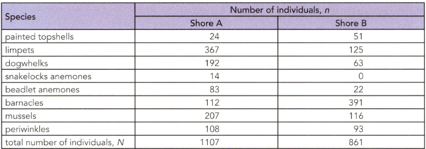
The Simpsons diversity Index of Shore A is 0.80 and the diversity of Shore B is 0.73. Compare the diversity of two shores.
In a survey of trees in a dry tropical forest. Some students identified five tree species (A to E). They counted the numbers of trees in an area 100m * 1oo m. Their results are as follows:
A 56 B 48 C 12 D 6 E 3
Calculate the Simpson’s index for the trees within the area sampled.
In a survey of trees in a dry tropical forest. Some students identified five tree species (A to E). They counted the numbers of trees in an area 100 m * 100 m. Their results are as follows:
| Species | No. of individuals |
| A | 56 |
| B | 48 |
| C | 12 |
| D | 6 |
| E | 3 |
Looking at table write a set of instructions for making a kite diagram
