A typical kinetic energy for a nucleon in a middle-mass nucleus may be taken as . To what effective nuclear temperature does this corresponds, based on the assumptions of the collective model of nuclear structure?

Important Questions on Nuclear Physics
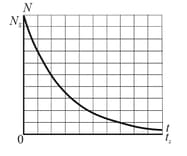
Figure shows the decay of parents in a radioactive sample. The axes are scaled by and . What is the activity of the sample at ?
The isotope decays to with a half-life of . Although the decay occurs in many individual steps, the first step has by far the longest half-life. Therefore, one can often consider the decay to go directly to Lead. That is,
various decay products.
A rock is found to contain of and of . Assume that the rock contained no Lead at formation, so all the Lead present later arose from the decay of Uranium. How many atoms of (a) and (b) does the rock contain later? (c) How many atoms of did the rock contain at formation ? (d) What is the age of the rock?
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an alpha particle. Consider the decays
and
Calculate the -value for the (a) first and (b) second decay, and determine that both are energetically possible. (c) The Coulomb barrier height for the alpha-particle emission is . What is the barrier height for emission? (Be careful about the nuclear radii). The needed atomic masses are:
.
Some radionuclide decay by capturing one of their own atomic electrons, a -shell electron, say. An example is
, .
Show that the disintegration energy for this process is given by
,
where and are the atomic masses of and , respectively, and is the binding energy of vanadium -shell electron. (Hint: Put and as the corresponding nuclear masses and then add in enough electrons to use the atomic masses).
