A uniform rod of mass and length lies at rest on a smooth horizontal table. A perfectly elastic particle of same mass , moving with speed on the table in a direction perpendicular to the rod, strikes one end of the rod. The kinetic energy generated in the rod is
Important Questions on Rotational Motion
A bullet of mass is fired horizontally into a large sphere of mass and radius resting on a smooth horizontal table.
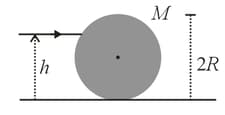
The bullet hits the sphere at a height from the table and sticks to its surface. If the sphere starts rolling without slippng immediately on impact, then
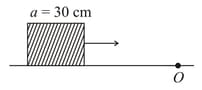
A cubical block of side is moving with velocity on a smooth horizontal surface. The surface has a bump at a point as shown in the figure. The angular velocity (in rad/s) of the block immediately after it hits the bump, is :
Assertion If the ice on the polar caps of the earth melts, then length of the day will increase.
Reason Moment of inertia of earth increases, as ice on polar caps melts.
The correct answer is
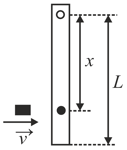
A thin rod of mass and length is suspended, at rest, from one end so that it can freely oscillate in the vertical plane. A particle of mass moving in a straight line with velocity hits the rod at its bottom most point and sticks to it (see figure). The angular speed (in ) of the rod immediately after the collision will be …………
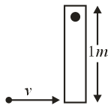
A rod of mass and length pivoted at one of its ends, is hanging vertically. A bullet of the same mass moving at speed strikes the rod horizontally at a distance from its pivoted end and gets embedded in it. The combined system now rotates with an angular speed about the pivot. The maximum angular speed is achieved for . Then
Two thin circular discs of mass and , having radii of and , respectively, are rigidly fixed by a massless, right rod of length through their center. This assembly is laid on a firm and flat surface, and set rolling without slipping on the surface so that the angular speed about the axis of the rod is . The angular momentum of the entire assembly about the point is (see the figure). Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true?
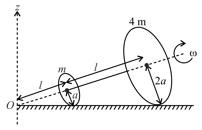
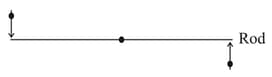
A rigid uniform rod of mass and length is resting on a smooth horizontal table. It is pivoted at its centre. Two marbles each of mass moving with uniform speed in the plane of the table collide with the two ends of the rod simultaneously as shown in the figure. The marbles stuck to the rod and continue to move with the rod. Time taken by the rod to rotate through an angle radian is (in seconds)