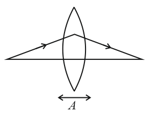
An achromatic doublet of focal length 90 cm si to be made of two lens. The material of one of the lenses has 1.5 times the dispersive power of the other. The doublet is converting type. Find the focal length of each lens.
Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
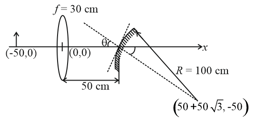
A small object is placed to the left of thin convex lens of focal length . A convex spherical mirror of radius of curvature is placed to the right of the lens at a distance of . The mirror is tilted such that the axis of the mirror is at an angle to the axis of the lens, as shown in the figure. If the origin of the coordinate system is taken to be at the centre of the lens, the coordinates (in ) of the point at which the image is formed are:
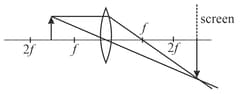
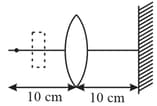
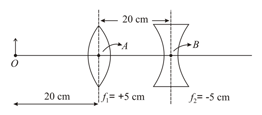
If the whole set up is immersed in water without disturbing the object and the screen positions, what will one observe on the screen?
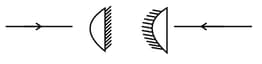
The word KVPY is written on board and viewed through different lenses such that board is at a distance beyond the focal length of the lens.
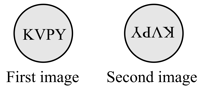
Ignoring magnification effects, consider the following statements.
First image has been viewed from the planar side of a plano-concave lens and second image from the planar side of a plano-convex lens.
First image has been viewed from the concave side of a plano-concave lens and second image from the convex side of a plano-convex lens.
First image has been viewed from the concave side of a plano-concave lens and second image from the planar side of a plano-convex lens.
First image has been viewed from the planar side of a plano-concave lens and second image from the convex side of a plano-convexlens.
Which of the above statements are correct?