MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
An alternating current, measured in amperes (A), is represented by the equation: . Sketch a graph to represent the current.

Important Questions on Alternating Currents
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
An alternating voltage , in volt , is represented by the equation:
(a) Determine the values of for this alternating voltage.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
An alternating voltage , in volt , is represented by the equation:
(b) Calculate when . (Remember that is in radians when you calculate this.)
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
An alternating voltage , in volt , is represented by the equation . Sketch a graph to show two complete cycles of this voltage.
MEDIUM
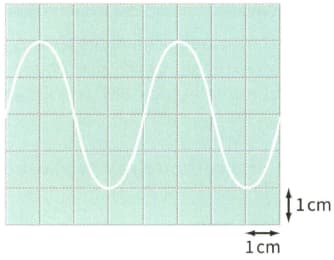
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The Y-sensitivity and time-base settings are and . The trace seen on the screen is the one shown in Figure .
Determine the amplitude, period and frequency of the signal applied to the -input of the .
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Sketch the CRO trace for a sinusoidal voltage of frequency and ampli tude , when the time-base is and the -sensitivity is .
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The alternating current (in ampere, A) in a resistor is represented by the equation: Calculate the r.m.s. value for this alternating current.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The mains supply to domestic consumers in many European countries has an r.m.s. value of for the alternating voltage. (Note that it is the r.m.s. value that is generally quoted, not the peak value.) Calculate the peak value of the alternating voltage.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Calculate the average power dissipated in a resistor of resistance . When a sinusoidal alternating current has a peak value of .
