An ice block floating in a river is pushed through a displacement along a straight embankment by rushing water, which exerts a force on the block. How much work does the force do on the block during the displacement?

Important Questions on Kinetic Energy and Work
A particle travels through a three-dimensional displacement given by If a force of magnitude
and with fixed orientation does work on the particle, find the angle between the force and the displacement if the change in the particle's kinetic energy is (a) and (b) .
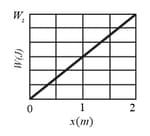
A can of bolts and nuts is pushed along the -axis by a broom along a greasy (frictionless) floor of a car repair shop in a version of shuffleboard. The figure shown below gives the work done on the can by the constant horizontal force from the broom versus the can's position . The scale of the figure's vertical axis is set by, .
(a) What is the magnitude of that force?
(b) If the can had an initial kinetic energy of moving in the positive direction of the -axis, what is its kinetic energy at the end of ?
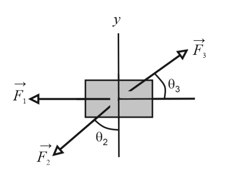
The figure shown below shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are and and the indicated angles are , . What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first of displacement?
(Given:- )
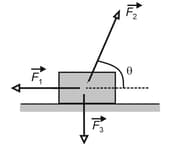
In the figure shown below the three forces applied to a trunk that moves leftward by over a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are and and the indicated angle is During the displacement,
(a) what is the net work done on the trunk by the three forces and (b) does the kinetic energy of the trunk increase or decrease?
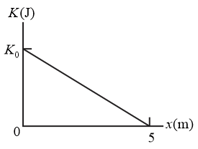
A object is moving in the positive direction of an -axis. When it passes through , a constant force directed along the axis begins to act on it. The figure shown below gives its kinetic energy versus position , as it moves from to ,. The force continues to act. What is when the object moves back through ?