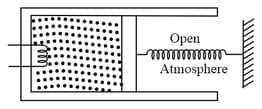
An ideal monatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-loaded massless piston of cross-section . The piston can slide on the walls of the cylinder without any friction. Initially, the gas is at and occupies a volume of and the spring is in its relaxed position. Now, gas is slowly heated by a small electric heater and the piston moves out slowly by . Calculate the final temperature of the gas and the heat supplied by the heater. The force constant of the spring is and atmospheric pressure is .

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
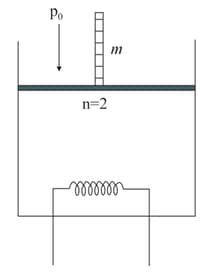
Two moles of an ideal monatomic gas are contained in a vertical cylinder of cross-sectional area as shown in the figure. The piston is frictionless and has a mass At a certain instant, a heater starts supplying heat to the gas at a constant rate watt. Find the velocity of the piston under isobaric condition. All the boundaries are adiabatic in nature.
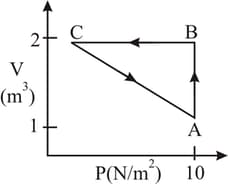
An ideal gas is taken through the cycle as shown in the fig. If the net heat supplied to the gas in the cycle is the work done by the gas in the process is:
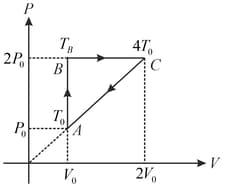
One mole of a gas is subjected to two process and one after the other as shown in the figure. is represented by, . We can conclude that (where, temperature, work done by gas, volume and internal energy),
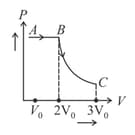
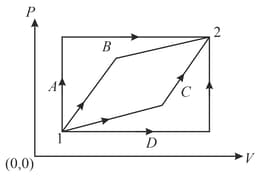
An ideal gas is taken from state to state through optional path and , as shown in the diagram. Let and represent the heat supplied, work done and change in internal energy of the gas, respectively. Then,