MEDIUM
Physics
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
An ideal monatomic gas is confined in a cylinder by a spring-loaded piston of cross section . Initially the gas is at and occupies a volume of and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is heated by a small heater until the piston moves out slowly by . The final temperature of the gas is . Find the value of . The force constant of the spring is , and the atmospheric pressure is . The cylinder and the piston are thermally insulated. The piston and the spring are massless and there is no friction between the piston and the cylinder. Neglect any heat-loss through the lead wires of the heater. The heat capacity of the heater coil is negligible.
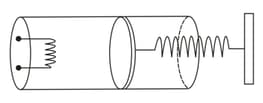

100% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
MEDIUM
Physics
IMPORTANT
Consider a vertical tube open at both ends. The tube consists of two parts, each of different cross-sections and each part having a piston which can move smoothly in respective tubes. The two pistons are joined together by an inextensible wire. The combined mass of the two pistons is and area of cross-section of the upper piston is greater than that of the lower piston. Amount of gas enclosed by the pistons is one mole. When the gas is heated slowly, pistons move by . If the rise in the temperature of the gas is , where is universal gas constant. Find the value of . Use and outside pressure ).
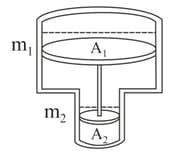
MEDIUM
Physics
IMPORTANT
moles of a gas in a cylinder under a piston are transferred to infinitely slowly from a state with a volume of and a pressure atoms to state with and a pressure as shown in figure. If the maximum temperature that the gas will reach in this process is , what is the value of
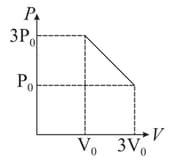
HARD
Physics
IMPORTANT
Given figure shows a horizontal cylindrical container of length , which is partitioned by a tight-fitting separator. The separator is diathermic but conducts heat very slowly. Initially the separator is in the state shown in the figure. The temperature of left part of cylinder is and that on right part is . Initially the separator is in equilibrium. As heat is conducted from right to left part, separator displaces to the right. Find the displacement of separator (in ) after a long time when gases on the two parts of cylinder are in thermal equilibrium.
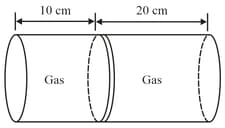
MEDIUM
Physics
IMPORTANT
An ideal gas has a volume at . It is confined by a spring-loaded piston in a vertical cylinder. Initially, the spring is in relaxed state. If the gas is heated to a final state of and pressure , find the work done (in ) on the spring (atmospheric pressure, ).
MEDIUM
Physics
IMPORTANT
Oxygen is filled in a closed metal jar of volume at a pressure of and temperature . The jar has a small leak in it. The atmospheric pressure is and the atmospheric temperature is . Find the mass (in ) of the gas that leaks out by the time the pressure and the temperature inside the jar equalise with the surrounding.
MEDIUM
Physics
IMPORTANT
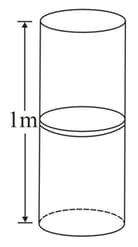
Figure shows a vertical cylindrical vessel separated in two parts by a frictionless piston free to move along the length of the vessel. The length of the cylinder is and the piston divides the cylinder in the ratio of . Each of the two parts of the vessel contains mole of an ideal gas. The temperature of the gas is in each part. Calculate the mass of the piston. (in )
EASY
Physics
IMPORTANT
One kilogram of a diatomic gas is at a pressure of . The density of the gas is . What is the energy of the gas due to its thermal motion?
EASY
Physics
IMPORTANT
Three perfect gases at absolute temperatures and are mixed. The masses of molecules are and and the number of molecules are and , respectively. Assuming no loss of energy, the final temperature of the mixture is
