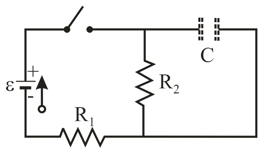
An isolated charged capacitor may gradually discharge as charge leaks from one plate to the other through the intermediate material, as if it were discharging through an external resistor. (a) What is the resistance of such an external resistor if a capacitor's potential difference decreases to of its initial value of in (b) What is the corresponding loss of potential energy in that time interval? (c) At the end of that interval, at what rate is the capacitor losing potential energy?

Important Questions on Circuits
In the following figure, the ideal batteries have EMFs and and the resistances are each . What is the current in (a) resistance and (b) resistance ?
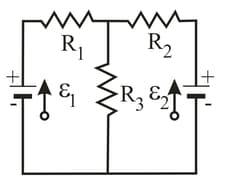
In the following figure, and both batteries are ideal. What is the rate at which energy is dissipated in (a) (b) and (c) ? What is the power of (d) battery 1 and (e) battery ? Is energy being absorbed or provided in (f) battery and (g) battery ?
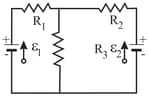
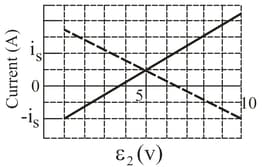
Both batteries in the following figure (a) are ideal. Emf of battery has a fixed value, but emf of battery can be varied between and . The plots in figure (b) give the currents through the two batteries as a function of The vertical scale is set by . You must decide which plot corresponds to which battery, but for both plots, a negative current occurs when the direction of the current through the battery is opposite the direction of that battery's emf. What are (a) emf (b) resistance and (c) resistance
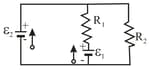
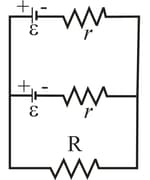
In the following figure, two batteries with emf and an internal resistance are connected in parallel across a resistance . (a) For what value of is the dissipation rate in the resistor a maximum? (b) What is that maximum?
Two identical batteries of emf and internal resistance are to be connected to an external resistance either in parallel (figure a) or in series (figure b). If , what is the current in the external resistance in the (a) parallel and (b) series arrangements? (c) For which arrangement is greater? If what is in the external resistance in the (d) parallel arrangement and (e) series arrangement? (f) For which arrangement is $i$ greater now?
(a)
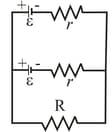
(b)
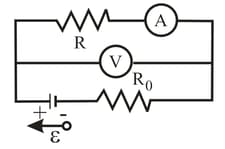
In figure a voltmeter of resistance and an ammeter of resistance are being used to measure a resistance in a circuit that also contains a resistance and an ideal battery with an emf of Resistance is given by where is the potential across and is the ammeter reading. The voltmeter reading is which is plus the potential difference across the ammeter. Thus, the ratio of the two meter readings is not but only an apparent resistance If . What are (a) the ammeter reading, (b) the voltmeter reading, and (c) ? (d) If $R_{\mathrm{A}}$ is decreased, does the difference between and increase, decrease, or remain the same?
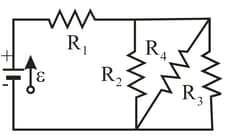
In the following figure, and the ideal battery has emf (a) What is the equivalent resistance? What is in (b) resistance (c) resistance (d) resistance and (e) resistance ?
In the following figure, , and the ideal battery has emf . First, the switch is closed a long time so that the steady state is reached. Then the switch is opened at time For resistor and at time what are (a) the current, (b) the rate at which the current is changing, and (c) the rate at which the dissipation rate is changing?