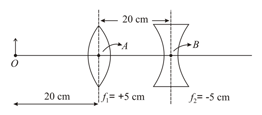
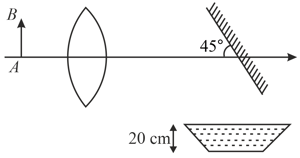
An object is at a distance of from a lens with focal length . A flat mirror turned through with respect to optical axis of the lens is placed at a distance behind the lens as shown in figure. A sharp image of the object is formed at the bottom of the vessel filled with water upto a height of . Find the distance of the image from the optical axis of the system .
Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
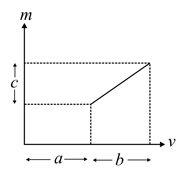
The graph shows how the magnification produced by a thin lens varies with image distance . The focal length of the lens used is
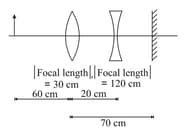
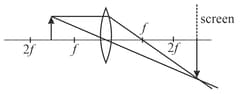
If the whole set up is immersed in water without disturbing the object and the screen positions, what will one observe on the screen?
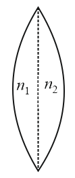
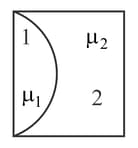
One plano-convex and one plano-concave lens of the same radius of curvature but of different materials are joined side by side as shown in the figure. If the refractive index of the material of is and that of is, then the focal length of the combination is:
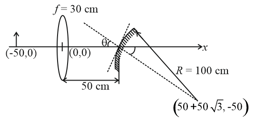
A small object is placed to the left of thin convex lens of focal length . A convex spherical mirror of radius of curvature is placed to the right of the lens at a distance of . The mirror is tilted such that the axis of the mirror is at an angle to the axis of the lens, as shown in the figure. If the origin of the coordinate system is taken to be at the centre of the lens, the coordinates (in ) of the point at which the image is formed are: