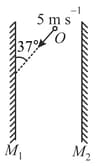
An object between two parallel (vertical) plane mirrors is approaching plane mirror as shown. If denote the magnitude of relative velocity of image with respect to object in mirror respectively and denotes relative velocity of approach of the images formed due to direct reflection by each mirror, then


Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
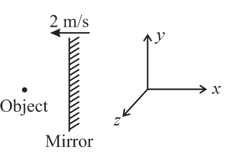
A plane mirror in - plane is moving with as shown. The object shown now starts moving with . What is the velocity of the image?
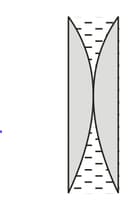
An equi-biconvex lens of focal length is cut into two parts and placed in contact as shown in the figure. A liquid of refractive index is filled between the two parts of lens. The equivalent focal length of the combination is (in )
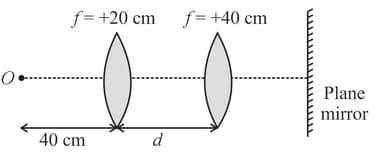
A convex lens of focal length and another convex lens of focal length are placed co-axially. What should be the distance (in ) between lenses so that final image of object is formed on itself?