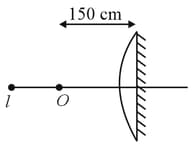
An object is placed in front of the curved surface of a planoconvex lens whose flat surface is silvered. A real image is formed in front of the lens. The focal length of the lens is


Important Questions on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
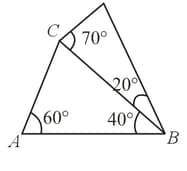
Two prisms of same glass are stuck together without gap as shown. Find the angle of incidence on the face such that the deviation produced by the combination is minimum
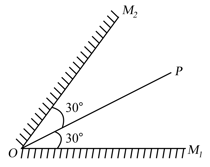
Two plane mirrors and intersecting at point forming an angle of The distance between the two direct images of a point object formed by them is The distance is
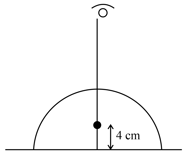
A hemispherical glass paper weight of radius contains a small air bubble located at a distance of from its flat surface on its axis of symmetry. What is apparent shift in the position of air bubble when it is looked by observer from top.
(Refractive index of glass )
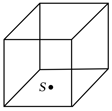
A glass cube of edge length placed on horizontal surface has a point source of light placed at centre of face. What should be minimum area to be covered on side faces so that no direct light comes out of the side faces.