Assertion: The mirror used in search light are parabolic and not concave spherical.
Reason: In a concave spherical mirror the image formed is always virtual.
Important Questions on Reflection of Light
| Object pin | Convex Lens | Convex Mirror | Image Pin |
| 22.2 cm | 32.2 cm | 45.8 cm | 71.2 cm |
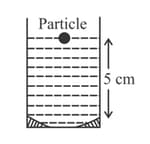
A point object is moving uniformly towards the pole of a concave mirror of focal length along its axis as shown below. The speed of the object is . At , the distance of the object from the mirror is . The average velocity of the image formed by the mirror between time and is:
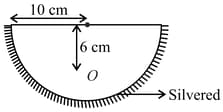
A hemispherical glass body of radius 10 cm and refractive index 1.5 is silvered on its curved surface. A small air bubble is 6 cm below the flat surface inside it along the axis. The position of the image of the air bubble made by the mirror is seen :
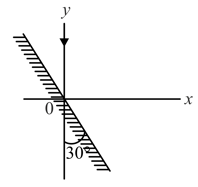
A mirror is placed at an angled of with respect to axis (see figure). A light ray travelling in the negative direction strikes the mirror. The direction of the reflected ray is given by the vector
| Column 1 | Column 2 | ||
| (A) | (a) | Convex mirror | |
| (B) | (b) | Concave mirror | |
| (C) | (c) | Real image | |
| (D) | (d) | Virtual image |
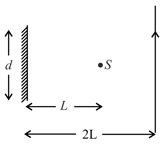
A point source of light, is placed at a distance in front of the center of plane mirror of width which is hanging vertically on a wall. A man walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror, at a distance as shown below. The distance over which the man can see the image of the light source in the mirror is:
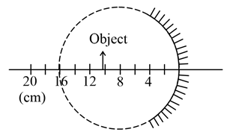
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere, if an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure down as schematic and not to scale)