At what distance from the centre of ring on axis, electric field is maximum :-
Important Questions on Electrostatics
Using Gauss law, derive expression for electric field due to a spherical shell of uniform charge distribution and radius at a point lying at a distance from the centre of shell, such that .
A solid metal sphere of radius having charge is enclosed inside the concentric spherical shell of inner radius and outer radius as shown in the figure. The approximate variation of electric field , as a function of distance , from centre , is given by:
Using Gauss law, derive expression for electric field due to a spherical shell of uniform charge distribution and radius at a point lying at a distance from the centre of shell, such that .
Electric intensity outside a charged cylinder having the charge per unit length at a distance from its axis is ____.
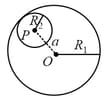
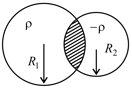
Two non-conducting spheres of radii and and carrying uniform volume charge densities and , respectively, are placed such that they partially overlap, as shown in the figure. At all points in the overlapping region,
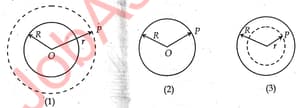
State Gauss's law in electrostatics and write in its mathematical form.Calculate the electric field at point due to charges this spherical shell, shown in figure (1) What will be the field shown in fig (2) and (3)? Given the surface charge density is .