At what distance should object kept to obtain image distance of thrice the focal length of diverging mirror?
Important Questions on Reflection and Spherical Mirror
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the figure from a hollow glass sphere, if an object is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be the nature and magnification of the image of the object? (Figure down as schematic and not to scale)
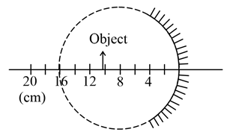
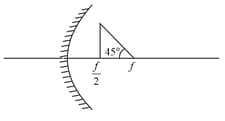
(Graphs are drawn schematically and are not to scale)
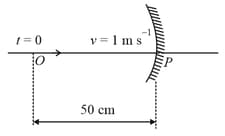
A point object is moving uniformly towards the pole of a concave mirror of focal length along its axis as shown below. The speed of the object is . At , the distance of the object from the mirror is . The average velocity of the image formed by the mirror between time and is:
| Object pin | Convex Lens | Convex Mirror | Image Pin |
| 22.2 cm | 32.2 cm | 45.8 cm | 71.2 cm |
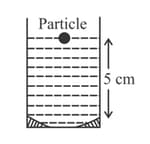
A particle is oscillating on the -axis with an amplitude about the point with a frequency. A concave mirror of focal length is placed at the origin (see figure).
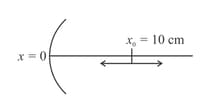
Identify the correct statements?
(i) The image executes periodic motion.
(ii) The image executes non-periodic motion.
(iii) The turning points of the image are asymmetric with respect to the image of the point at .
(iv) The distance between the turning points of the oscillation of the image is .
Only paraxial rays are considered for the formation of image in spherical mirrors because-

