Boron is an element in Group 13 of the Periodic Table.
Boron has two isotopes.
Deduce the number of i) protons, ii) neutrons and iii) electrons in one neutral atom of the isotope .

Important Questions on Atomic Structure
Boron is an element in Group 13 of the Periodic Table.
Boron has two isotopes.
What do you understand by the term isotope?
Boron is an element in Group 13 of the Periodic Table. Boron has two isotopes.
State the relative masses and charges of i) an electron ii) a neutron iii) a proton
Zirconium, , and hafnium, , are metals. An isotope of zirconium has 40 protons and 91 nucleons.
i) Write the isotopic symbol for this isotope of zirconium.
ii) State the number of neutrons present in one atom of this isotope.
Zirconium, , and hafnium, , are metals.
The symbol for a particular ion of hafnium ion is . Deduce the number of electrons that are present in one of these hafnium ions.
Zirconium, , and hafnium, , are metals.
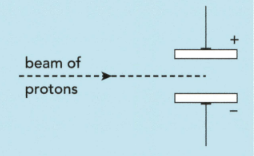
The subatomic particles present in zirconium and hafnium are electrons, neutrons and protons. A beam of protons is fired into an electric field produced by two charged plates, as shown in the diagram.
i) Describe how the beam of protons behaves when it passes through the gap between the charged plates.
ii) Explain your answer.
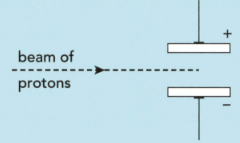
The subatomic particles present in zirconium and hafnium are electrons, neutrons and protons. Describe and explain what happens when a beam of neutrons passes through the gap between the charged plates instead of protons in the figure: