Calculate the velocity of efflux of water when a completely filled cylinder of height is punched with a hole on the side wall near its bottom. (Take, .)
Important Questions on Fluid Mechanics
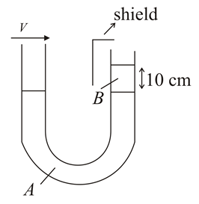
A -tube open at both the ends is partially filled with a liquid of density . Another liquid of density is poured into one of the arms and it forms a column of length as shown in the figure. If the arm into which liquid is poured is shielded from any air motion, the speed with which air should be blown across the top of the other arm till the levels of the two liquids are at same height in is (Density of air is , Acceleration due to gravity )
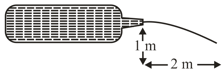
A bottle has a thin nozzle on top. It is filled with water, held horizontally at a height of and squeezed slowly by hands so that the water jet coming out of the nozzle hits the ground at a distance of If the area over which the hands squeeze it, is the force applied by hands is close to: (take and density of water )
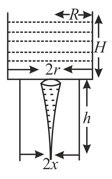
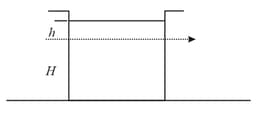
Consider a water jar of radius R that has water filled up to height H and is kept on a stand of height h (see figure). Through a hole of radius r at its bottom, the water leaks out and the stream of water coming down towards the ground has a shape like a funnel as shown in the figure. If the radius of the cross-section of water stream when it hits the ground is x. Then:
Water flows through a pipe as shown in the figure. The areas of cross-section of sections and respectively are and . The gauge pressure in the pipe at the centre of section is and the flow rate is . The difference in heights of the water levels in the vertical pipes is_____ . (Acceleration due to gravity )
The platelets are drifting with the blood flowing in a streamline flow through a horizontal artery as shown below:
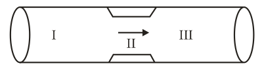
Artery is contracted in region . Choose the correct statement.
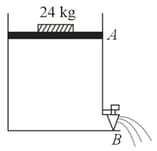
Consider a water tank as shown in the figure. It's cross-sectional area is . The tank has an opening near the bottom whose cross-section area is . A load of is applied on the water at the top when the height of the water level is above the bottom, the velocity of water coming out the opening is . The value of , to the nearest integer, is ___ .[Take the value of to be ]
A cylindrical container containing water has a small hole at height of from the bottom and at a depth of from the top surface of the liquid. The maximum horizontal distance travelled by the water before it hits the ground is
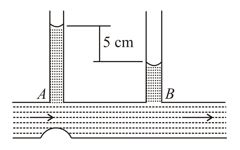
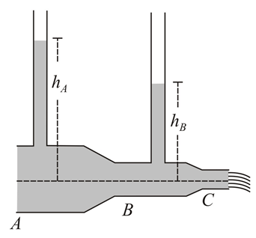
In the diagram shown, the difference in the two tubes of the manometer is , the cross-section of the tube at and is and respectively. The rate at which water flows through the tube is

