Cell M now divides by meiosis.
Outline three differences between the division of meiosis and mitosis.

Important Questions on Inheritance
State three features, visible in figure 16.2, that show that the fruit fly is an insect.
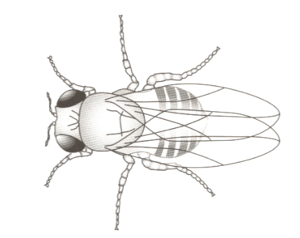
Fruit flies can have normal wings or vestigial (really small) wings. The allele for normal wings, N, is dominant. The allele for vestigial wings, n, is recessive.
Complete the table to show the possible genotype and phenotypes for fruit fly wings. Be very careful to write the letters N and n so that there is no doubt whether each one is a capital letter or a small letter.
| Genotype | Phenotype |
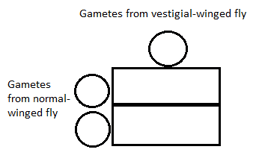
Complete the genetic diagram to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring of a heterozygous normal-winged fly and a vestigial-winged fly.
Phenotypes of parents: normal wings vestigial wings
Genotypes of parents: _____ _____
Gametes: _____ and _____ all _____
The family tree (pedigree) in figure 16.3 shows the incidence of a genetic disease called phenylketonuria (PKU) in four generations of a family.
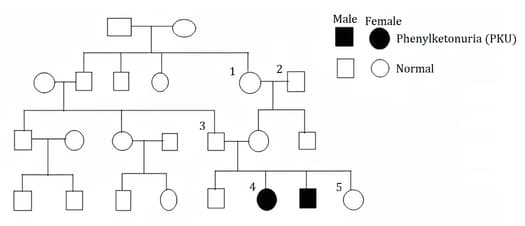
Describe one piece of evidence from the diagram that suggests PKU is caused by a recessive allele.
The family tree (pedigree) in figure 16.3 shows the incidence of a genetic disease called phenylketonuria (PKU) in four generations of a family.
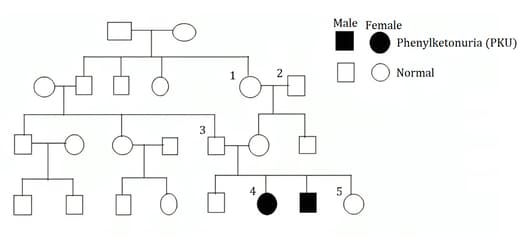
If PKU is caused by a recessive allele, explain why it is unlikely that this allele first appeared in person 4.
The family tree (pedigree) in figure 16.3 shows the incidence of a genetic disease called phenylketonuria (PKU) in four generations of a family.
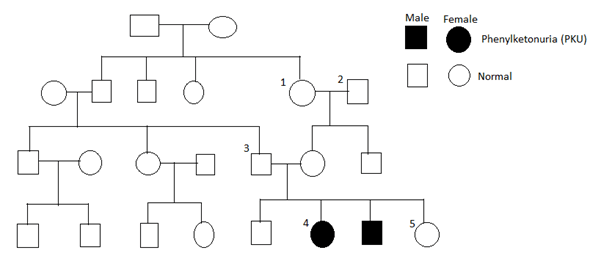
In the space below, deduce the possible genotypes of person 1, 2, 3 and 4. Use the symbol q for the PKU allele and the symbol Q for the normal allele.
