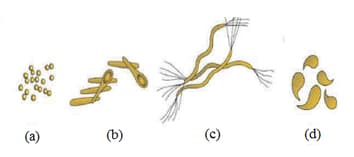
Conjugation in . coli is a microbial process wherein conjugative plasmids are transferred from one bacterium to another that does not possess it. This requires physical contact between the cells involved in the transfer. In an experiment performed in a sterilized U-tube, strains (resistance to ampicillin encoded in its plasmid) and (resistance to tetracycline encoded in its genome) were grown in an appropriate medium without an antibiotic. A pore size nitrocellulose membrane placed in between the two arms serves as a partition. In a parallel identical experiment the membrane was replaced by a nitrocellulose membrane. After allowing enough time for the conjugation process to occur, an aliquot from each arm is plated on either ampicillin or tetracyclin antibiotic containing plate. Choose the correct statement about the outcome of the experiment.

Important Questions on Biodiversity
Match the following lists:
| List-I | List-II | ||
| (A) | Photoautotroph | (I) | Nitrosomonas |
| (B) | Chemoautotroph | (II) | Rhodospirillum |
| (C) | Photoheterotroph | (III) | Salmonella |
| (D) | Chemoheterotroph | (IV) | Chlorobium |
The correct match is:
I. Cyanobacteria are referred to as blue-green algae.
II. They perform oxygenic photosynthesis in chloroplasts.
II. The red-colour of red-sea is due to the presence of a cyanobacterial species Trichodesmium erythraeum.
IV. All the cyanobacterial species can fix atmospheric in specialised cells called heterocysts.
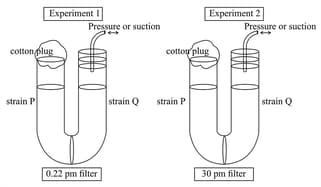
Bacteria are grouped under four categories based on their shape. Study the given figure and identify A. B. C and D?