EASY
Earn 100
Consider a catalyzed reaction and are the rate constants for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions, respectively. However, the catalyst becomes inactive at temperature . The graph(s) that reasonably depict(s) the temperature dependence of the overall rate constant is/are
(a)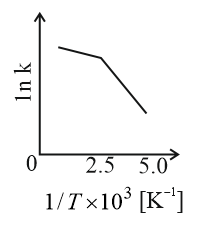

(b)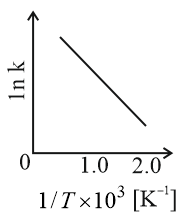

(c)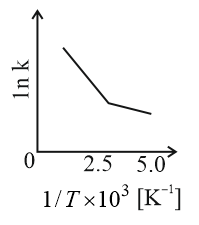

(d)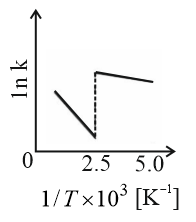

50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Chemical Kinetics
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
The Arrhenius plots of two reactions, I and II are shown graphically-
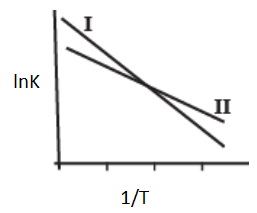
The graph suggests that-
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
The activation energy of the backward reaction exceeds that of the forward reaction by (in ). If the pre-exponential factor of the forward reaction is times that of the reverse reaction, the absolute value of for the reaction at is ____.
(Given; and is the Gibbs energy)
EASY
HARD
HARD
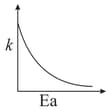
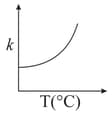
Consider the given plots for a reaction obeying Arrhenius equation (and are rate constant and activation energy, respectively )
(I)
(II)
MEDIUM
A sample of milk splits after at and after at when the population of Iactobacillus acidophilus in it doubles. The activation energy (in ) for this process is closest to ______________.
MEDIUM
(Assume Activation energy and pre-exponential factor are independent of temperature; )
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
[Gas constant, ]
MEDIUM
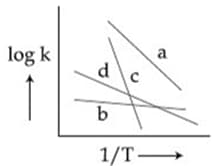
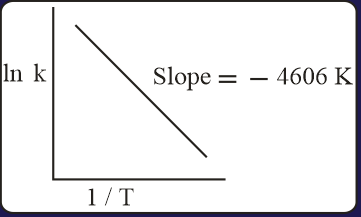
For a reaction, consider the plot of versus given in the figure. If the rate constant of this reaction at is , then the rate constant at is:
HARD

