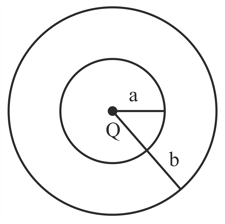
Consider a uniformly charged, insulating sphere of radius . The total amount of charge on the sphere is . What is the total electrical flux in through a spherical surface of radius that is concentric with the insulating sphere? Round off to nearest integer.
Important Questions on Electrostatics
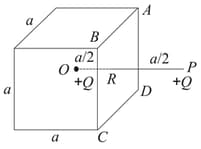
Consider a region in free space bounded by the surfaces of an imaginary cube having sides of length as shown in the figure. A charge is placed at the centre of the cube. is such a point outside the cube that the line perpendicularly intersects the surface at and also . A charge is placed at point also. What is the total electric flux through the five faces of the cube other than
for
for .
does not depend on x and y. If this potential is generated by a constant charge per unit volume (in units of ) which is spread over a certain region, then choose the correct statement.
Given below are two statements
Statement : An electric dipole is placed at the centre of a hollow sphere. The flux of electric field through the sphere is zero, but the electric field is not zero anywhere in the sphere.
Statement : If is the radius of a solid metallic sphere and be the total charge on it. The electric field at any point on the spherical surface of radius is zero but the electric flux passing through this closed spherical surface of radius is not
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
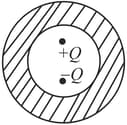
Arrangement of charges are shown in the figure. Flux linked with the closed surface and respectively are ________ and ________ .
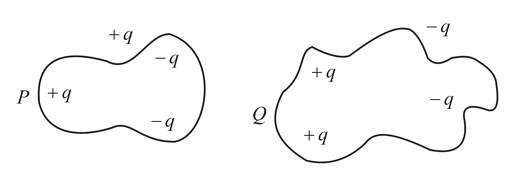
The following figure shows two point charges and and a metal rod of length carrying a charge with a part of its length inside a cubical box. The electric flux linked with the box will be,
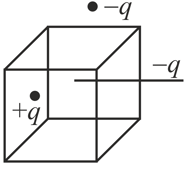
What is the electric flux for Gaussian surface A that encloses the charged particles in free space? [Given:

Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) The electric lines of force entering into a Gaussian surface provide negative flux.
(b) A charge is placed at the centre of a cube. The flux through all the faces will be the same.
(c) In a uniform electric field net flux through a closed Gaussian surface containing no net charge, is zero.
(d) When an electric field is parallel to a Gaussian surface, it provides a finite non-zero flux.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: