MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Construct a diagram to show how the water potential of the blood is controlled. In your diagram, identify the following: receptors, input, effector and output. Indicate clearly how different parts of the body are coordinated and show how negative feedback is involved.

Important Questions on Homeostasis
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Describe the problems that would occur if the water potential of blood plasma was not controlled and not kept within narrow limits.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
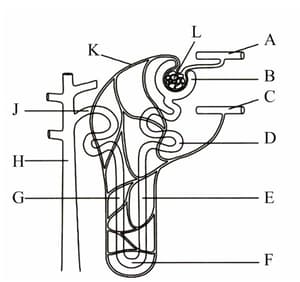
Explain the functional advantage of the parallel arrangement of structures E, G and H in the medulla of the kidney.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Describe and explain the concentrations of fluid in the proximal convoluted tubule and in the collecting duct.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
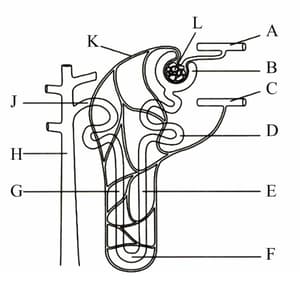
Describe how ADH acts as a cell-signalling compound.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
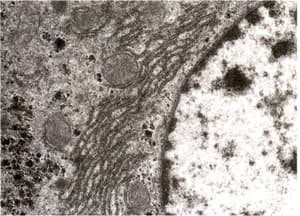
Identify the structures in the liver cell visible in the given figure. Suggest the roles of the structures in liver cells.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Explain why signal amplification in liver cells is necessary in the control of blood glucose.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Outline the role of the kidneys in homeostasis.
MEDIUM
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Explain how the cells lining of collecting ducts determine the concentration of the urine that enters the renal pelvis of the kidney.
