EASY
Earn 100
and denote the molar specific heat capacities of a gas at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. Then
(a) is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monoatomic ideal gas
(b) is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monoatomic ideal gas
(c) is larger for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monoatomic ideal gas
(d) is smaller for a diatomic ideal gas than for a monoatomic ideal gas
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
What will be the molar specific heat at constant volume of an ideal gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules?
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
(Take gas constant )
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Two different metal bodies and of equal mass are heated at a uniform rate under similar conditions. The variation of temperature of the bodies is graphically represented as shown in the figure. The ratio of specific heat capacities is:
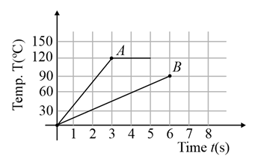
MEDIUM
[Given that
EASY
EASY

