Describe hybridisation in the case of and . The axial bonds are longer as compared to equatorial bonds in whereas in both axial bonds and equatorial bonds have the same bond length. Explain.

Important Questions on Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
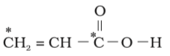
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
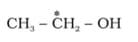
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
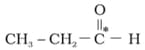
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
Molecular orbitals are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Two atomic orbitals combine to form two molecular orbitals called bonding molecular orbital (BMO) and antibonding molecular orbital (ABMO). The energy of antibonding orbital is raised above the parent atomic orbitals that have combined and the energy of the bonding orbital is lowered than the parent atomic orbitals. Energies of various molecular orbitals for elements hydrogen to nitrogen increase in the order :
and for oxygen and fluorine order of energy of molecular orbitals is given below :
Different atomic orbitals of one atom combine with those atomic orbitals of the second atom which have comparable energies and proper orientation. Further, if the overlapping is head-on, the molecular orbital is called Sigma and if the overlap is lateral, the molecular orbital is called pi. The molecular orbitals are filled with electrons according to the same rules as followed for filling of atomic orbitals. However, the order for filling is not the same for all molecules or their ions. Bond order is one of the most important parameters to compare the strength of bonds.
Which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following pair is expected to have the same bond order?
