Differentiate between centre of mass and centre of gravity.
Important Questions on Laws of Motion
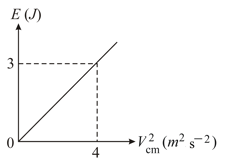
In figure and represent the total energy and speed of centre of mass of an object of mass in pure rolling. The object is:
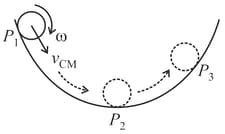
A small ring is rolling without slipping on the circumference of a large bowl as shown below in the figure. The ring is moving down at , comes down to the lower most point and is climbing up at . Let denote the velocity of the centre of mass of the ring. Choose the correct statement regarding the frictional force on the ring.
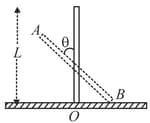
A plank is moving in a horizontal direction with a constant acceleration . A uniform rough cubical block of side rests on the plank and is at rest relative to the plank.
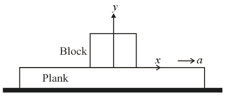
Let the centre of mass of the block be at at a given instant. If , then the normal reaction exerted by the plank on the block at that instant acts at
If the sum of external forces acting on a system is zero, then the centre of mass
Two masses and , each of mass are fixed together by a massless spring, A force acts on the mass as shown in figure. If the mass starts moving away from mass with acceleration , then the acceleration of mass will be :
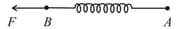
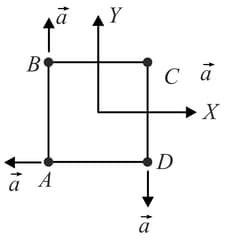
Four particles and with masses and are at the corners of a square. They have accelerations of equal magnitude with directions as shown. The acceleration of the centre of mass of the particles is:
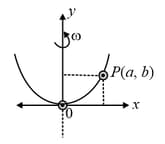
A bead of mass stays at point on a wire bent in the shape of a parabola and rotating with angular speed (see figure). The value of is (neglect friction)
Shown in the figure is rigid and uniform one meter long rod held in horizontal position by two strings tied to its ends and attached to the ceiling. The rod is off mass and has another weight of mass hung at a distance of from . The tension in the string at is:
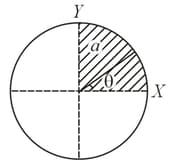
The disc of mass with uniform surface mass density is shown in the figure. The centre of mass of the quarter disc (the shaded area) is at the position where is _______ . (Round off to the Nearest Integer) [ is an area as shown in the figure]
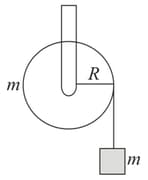
A mass is supported by a massless string wound around a uniform hollow cylinder of mass and radius . If the string does not slip on the cylinder, then with what acceleration will the mass release? (Assume acceleration due to gravity)