Ethanol of density flows smoothly through a horizontal pipe that tappers in cross- sectional area from to . The pressure difference between the wide and the narrow sections of pipe is . What is the volume flow rate of ethanol in multiples of .

Important Questions on Properties of Solid and Liquid
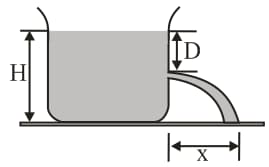
A glass tube has three different cross sectional areas with the values indicated in the figure. A piston at the left end of the tube exerts pressure so that the mercury within the tube flows from the right end with a speed of . Three points within the tube are labeled and . The atmospheric pressure is ; and the density of mercury is (use ):
The pressure at point is equal to
The free surface of a liquid at rest kept in a container of reasonably large size is always seen to be horizontal. This is due to
(I) the absence of relative velocity between the liquid and the container
(ii) the absence of relative acceleration between the liquid and the container
(iii) gravitational energy is constant on a horizontal surface
(iv) Bernoulli's theorem
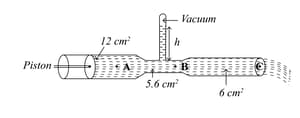
The velocities of the liquid which flows in the two sections of a horizontal tube have areas of cross-section and , are and respectively. The difference in the levels of the liquid in the two vertical tubes is . Then
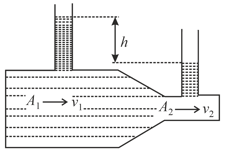
A cylindrical container containing water has a small hole at height of from the bottom and at a depth of from the top surface of the liquid. The maximum horizontal distance travelled by the water before it hits the ground is
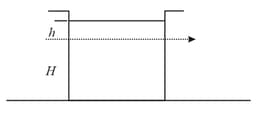
A tank is filled with water up to a height . Water is allowed to come out of a hole Pin one of the walls at a depth below the surface of the water. Express the horizontal distance in terms of and .