EASY
Earn 100
Examples of strong analgesics are morphine, codeine, and diamorphine (heroin). Identify two functional groups present in all three of these analgesics.
Important Questions on Medicinal Chemistry
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
Methadone is an analgesic that is commonly used in the treatment of opioid dependence. The structure of methadone is given in figure.
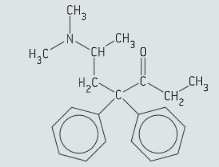
State the names of two functional groups in the molecule of methadone.
EASY
Methadone is an analgesic that is commonly used in the treatment of opioid dependence. The structure of methadone is given in figure.
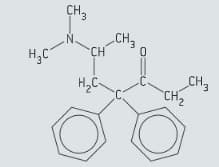
Identify by marking it with an asterisk (*) on a copy of figure, the chiral carbon atom in methadone.
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY

