Explain Cartesian sign convention for spherical mirrors.
Important Questions on Light
If a mirror forms erect image for objects placed between pole and focus, and it forms real-inverted image for object placed anywhere between focus and infinity, then the mirror is:
The radius of curvature of a converging mirror is . At what distance from the mirror should an object be placed so as to obtain a virtual image?
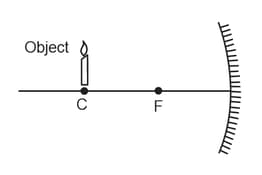
Which of the following statements is not true in reference to the diagram shown above?
A student holding a mirror in his hand, directed the reflecting surface of the mirror towards the Sun. He then directed the reflected light on to a sheet of paper held close to the mirror.
Which type of mirror does he have?
Write the sign convention for reflection by spherical mirrors.
An object of height is kept at a distance of from the pole of a diverging mirror. If the focal length of the mirror is , the height of the image formed is ____.
What should he do to burn the paper?
Establish the relation between the radius of curvature and focal length of the spherical concave mirror.
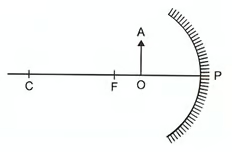
For the diagram shown, according to the new Cartesian sign convention the magnification of the image formed will have the following specifications.
A student holding a mirror in his hand, directed the reflecting surface of the mirror towards the Sun. He then directed the reflected light on to a sheet of paper held close to the mirror.
Will he be able to determine the approximate value of focal length of this mirror from this activity ? Give reason and draw ray diagram to justify your answer in this case.

