HARD
Earn 100
Explain Maxwell distribution of molecular speeds with necessary graph.
Important Questions on Kinetic Theory
HARD
HARD
Consider an ideal gas confined in an isolated closed chamber. As the gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion, the average time of collision between molecules increases as , where is the volume of the gas. The value of is:
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
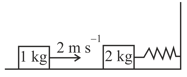
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
Boltzmann Constant
Avogadro number
Radius of Earth:
Gravitational acceleration on Earth
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY

