HARD
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Explain refraction of light on the basis of wave theory. Hence prove the laws of refraction.

Important Questions on Wave Optics
MEDIUM
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
A slit 4 cm wide is irradiated with microwaves of wavelength 2 cm. Find the angular spread of the central maximum assuming normal incidence to the plane of the slit.
MEDIUM
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
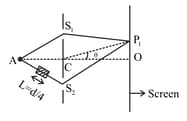
A small transparent slab containing material of is placed along . What will be the distance from of the principal maxima and of the first minima on either side of the principal maxima obtained in the absence of the glass slab.
HARD
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
HARD
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
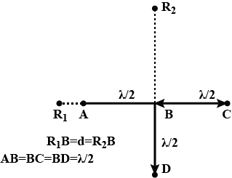
the two coherent sources at point on the screen is and at a point on the screen is How many bright and dark bands are observed between the two points and (points and are on the opposite sides of central bright band).
HARD
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
HARD
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
HARD
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
12th Karnataka Board
IMPORTANT
Four identical monochromatic sources as shown in the figure produce waves of the same wavelength and are coherent. Two receiver and are at great but equal distances from . Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources or has been turned off?