Explain the need for a feedback circuit in a transistor oscillator.

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Electronics and Communication from Tamil Nadu Board Physics Standard 12 Vol II Solutions
(i) Basic components of a communication system
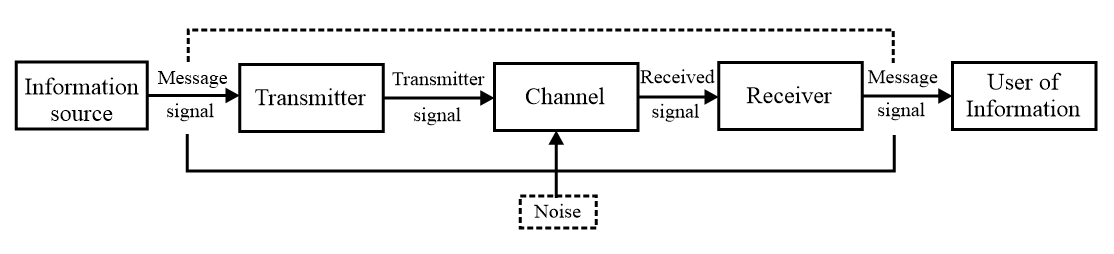
(ii) Transmitter: Transmitter converts the message signal produced by information source into a form (e.g. electrical signal) that is suitable for transmission.
(iii) Communication channel: Communication channel is a medium which connects a receiver and a transmitter. It carries the modulated wave from the transmitter to the receiver.
(iv) Receiver: It receives and decodes the signal into original form.
(v) Transducer is the device that converts one form of energy into another. Microphone, photo detectors and piezoelectric sensors are types of transducer.
2. Terms related to signals:
(i) Signal is the information converted in electrical form. Signals can be analog or digital. Sound and picture signals in TV are analog.
(ii) Analog Signal:- A continuously varying signal is called an analog signal. A decimal number with system base is used to deal with analog signals.
(iii) Digital Signal:- A signal that can have only discrete stepwise values is called a digital signal. A binary number system with base is used to deal with digital signals.
(iv) Noise: There are unwanted signals that tend to disturb the transmission and processing of message signals. The source of noise can be inside or outside the system.
(v) Attenuation: It is the loss of strength of a signal while propagating through a medium.
(vi) Amplification: It is the process of increasing the amplitude (and therefore the strength) of a signal using an electronic circuit called the amplifier. Amplification is absolutely necessary to compensate for the attenuation of the signal in communication systems.
(vii) Range: It is the largest distance between the source and the destination up to which the signal is received with sufficient strength.
(viii) Repeater: A repeater acts as a receiver and a transmitter. A repeater picks up the signal which is coming from the transmitter, amplifies and retransmits it with a change in carrier frequency.
3. Bandwidth:
Bandwidth of signals: Different signals used in a communication system such as voice, music, picture, computer data etc. All have different ranges of frequency. The difference of maximum and minimum frequency in the range of each signal is called bandwidth of that signal.
4. Propagation of electromagnetic waves:
(i) Ground Wave Propagation: The radio waves which travel through the atmosphere following the surface of earth are known as ground waves or surface waves and their propagation is called ground wave propagation or surface wave propagation. Due to these losses the ground waves are not suited for very long range communication. Ground wave propagation can be sustained only at low frequencies .
(ii) The sky waves are the radio waves of frequency between to . The ionospheric layer acts as a reflector for a certain range of frequencies. Therefore, it is also called ionospheric propagation or short wave propagation.
(iii) The space waves are the radio waves of very high frequency (i.e. between to or more.
5. Height of antenna:
Height of transmitting Antenna: The range of an antenna of height is given by, , where is the radius of the earth.
6. Modulation:
(i) The phenomenon of superposition of information signal over a high frequency carrier wave is called modulation. Amplitude, frequency and phase modulations are different kinds of modulations.
(ii) Uses of modulation: To avoid interference and distortion and to design antennas of practical size
(iii) Amplitude Modulation:
(iv) Frequency spectrum of AM wave:
(v) Frequency Modulation (FM): When the frequency of the carrying wave is changed in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal, it is called frequency modulation
(vi) Modulation factor:
7. Internet and GPS:
(i) Internet is the largest computer network recognized globally that connects millions of people through computers.
(ii) GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a global navigation satellite system that offers geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver on the earth.
