EASY
Earn 100
Explain the oxidation of phenol in the presence of chromyl chloride.
Important Questions on Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
MEDIUM
The functional group which is formed when Phenol is made to react with Chloroform in the presence of dilute Sodium hydroxide
EASY
MEDIUM
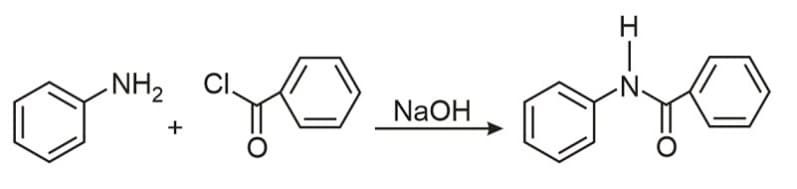
Is known by the name:
MEDIUM
HARD
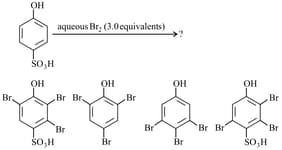
In the following reaction, the product(s) formed is/are:
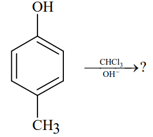
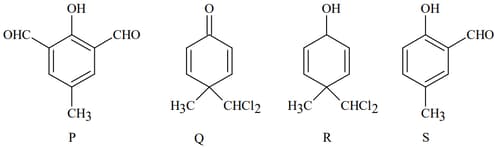
MEDIUM
HARD
The increasing order of the values of the following compounds is:
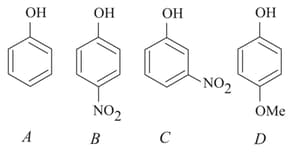
HARD
HARD
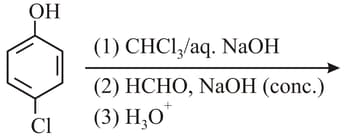
The major product(s) of the following reaction is/are:
HARD
What is in the following sequence of reactions?
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
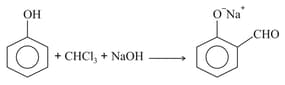
EASY
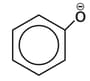 ion ?
ion ?MEDIUM
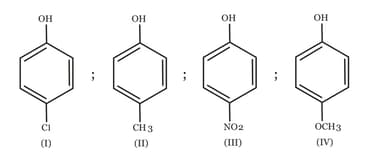
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
| Test | Inference | |
|---|---|---|
| Insoluble | ||
| Soluble | ||
| Decolourization |
HARD
HARD
HARD
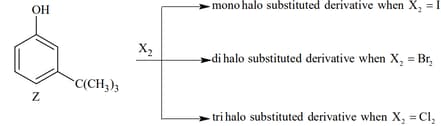
The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained by

