Explain what feature of the structure of glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) allows fatty acid molecules to become attached to it to make fats, and state the name of the reaction by which this occurs.

Important Questions on Biochemistry
Lactose is a typical disaccharide. Suggest a reason why fatty acids can be attached to it.
The fatty acids in olestra are smaller than those in cooking fats. Suggest a reason for this.
State the name of the two polymeric forms of starch.
Describe, in terms of polarity and solubility, the most common properties of vitamins A and D.
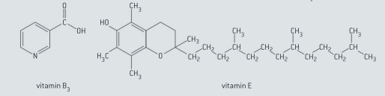
The formulae of vitamin (niacin) and vitamin (α-tocopherol) are given below.
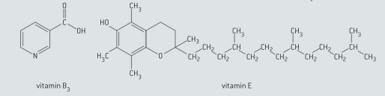
Identify two functional groups in vitamin and two functional groups in vitamin .
In the human body, vitamin E acts as antioxidant. Identify the functional group or groups that are responsible for anti oxidative properties of this vitamin.
Predict, with reference to functional groups and polarity, whether each of the following vitamins is water-soluble or fat soluble.
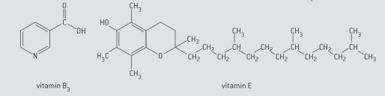
Suggest which vitamin ( or ) must be ingested regularly in small quantities and which one can be taken at much longer intervals but in larger amounts without any detrimental health effects.