Fermentation is
Important Questions on Respiration in Plants
Arrange the following in the order of their occurrence in the glycolytic pathway.
I. Triose bisphosphate Triose phosphate
II. Fructose--phosphate Fructose -bisphosphate
III. Phosphoenolpyruvate Pyruvic acid
IV. -Phosphoglycerate Phosphoenolpyruvate
V. Glucose--phosphate Fructose--phosphate
VI. Triose phosphate -Phosphoglycerate
The correct sequence is:
Arginosuccinase; Hexokinase; Glutamine synthetase
A) Glutamic acid
B) Arginine
C) Arginosuccinic acid
D) Glucose
E) Fructose-1,6 phosphate
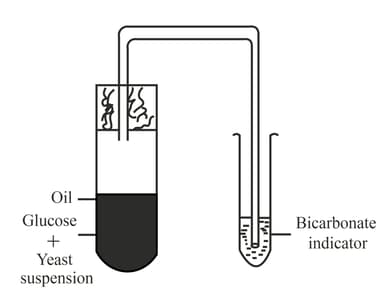
The figure given below is designed to show yeast respiration. In one of the tubes, there is yeast suspension in glucose solution. This solution was boiled before yeast was added to it. Which one of the following is the possible reason for boiling sugar solution?
Respective products released along with main product in biochemical reactions catalysed by given enzymes
A) Glutamine synthetase I) NADH + H+
B) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase II) ADP + Pi
C) Hexokinase III) Inorganic phosphate
D) Malate dehydrogenase IV) ADP
Assertion (A) :- The pathway from glucose to lactic acid occurs in metabolic steps. Organisms will trap this energy and store in the form of chemical molecules.
Reason (R) :- Glucose is the only substrate for the production of energy.
The correct option among the following is:
(A) Glycolysis has chain reactions.
(B) In glycolysis, ATP is utilised in one step.
(C) There is one step related to the formation of .
(D) Glycolysis can take place in the mitochondria matrix also.
| List-I | List-II | ||
| A | Phosphoenol pyruvate | I | Hexokinase |
| B | Pyruvic acid | II | Enolase |
| C | Triosephosphate | III | Pyruvic kinase |
| D | Glucose-—phosphate | IV | Aldolase |
The correct match is:
Assertion (): Anaerobic respiration yields less energy utilizing oxygen.
Reason (): In anaerobic respiration, energy is released due to the incomplete breakdown of organic molecules.
(A) Acetaldehyde Ethanol
(B) Glyceraldehyde Phosphate - phosphoglyceric acid
(C) Pyruvic acid lactic acid
(D) Oxalosuccinic acid ketoglutaric acid
(E) ketoglutaric acid succinyl

