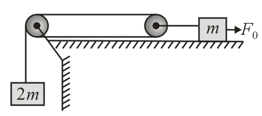
Find the tension needed to hold the cart in equilibrium, if there is no friction.


Important Questions on Laws of Motion
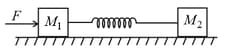
Two blocks of masses and are connected to each other through a light spring as shown in figure. If we push mass with force and cause acceleration in mass , what will be the magnitude of acceleration in ?
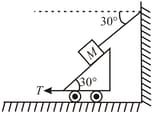
A mass lies on a fixed, smooth cylinder. An ideal string attached to passes over the cylinder to mass Then the value of angle for which system is in equilibrium
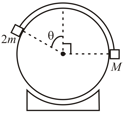
Figure shows a block of mass sliding on a block of mass Find the acceleration of each block. (All surface are smooth)
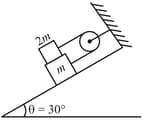
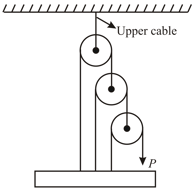
The pull is just sufficient to keep the block in equilibrium as shown. Pulleys are ideal. Find the tension (in ) in the upper cable connected with ceiling.
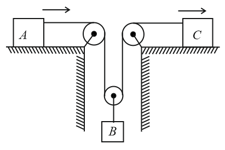
In the arrangement shown in figure . Pulleys are massless and string are light. For what value of the mass moves with constant velocity (Neglect friction)
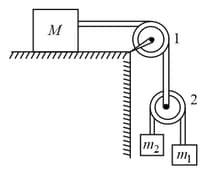
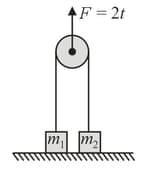
In the figure shown pulley is ideal. At both masses touches the ground and string is taut. A force $F=2 t$ is applied to pulley ( is in second) then is lifted off the ground at time
A block of mass on a smooth horizontal surface is connected to a second mass by a light cord over a light frictionless pulley as shown. (Neglect the mass of the cord and of the pulley). A force of magnitude is applied to mass as shown. Neglect any friction. Find the value of force for which the system will be in equilibrium.