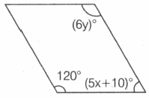
Find the value of and in the following parallelogram?

Important Points to Remember in Chapter -1 - Geometry from Arihant Expert Team Mathematics & Pedagogy CTET & TETs Class (VI-VIII) Solutions
Geometry
1. Conversions
miles
quintal
quintal tonne
pounds (approx.)
litre
acre
hectare
2. Sum of all the angles of a polygon with sides
3. Sum of all exterior angles of a polygon
4. Sum of all the angles of a triangle
Types of Triangle:
i. Acute angle triangle: Triangles which have all three angles acute (less than ).
ii. Obtuse angle triangle: Triangles which have one of the angles obtuse (more than ).
iii. Right angle triangle: Triangles which have one of the angles equal to .
iv. Equilateral triangle: Triangle with all sides equal. All the angles in such a triangle measure .
v. Isosceles triangle: Triangle with two of its sides equal, and consequently, the angles opposite to the equal sides are also equal.
vi. Scalene Triangle: Triangle with none of the sides equal to any other side.
5. The Sine Rule: ( Circum radius)
6. Area of a Triangle:
7. Area of a Triangle: where
8. Area of an Equilateral Triangle:
9. Congruency of Triangles: Two triangles are congruent if all the sides of one are equal to the corresponding sides of another. It follows that all the angles of one are equal to the corresponding angles of another.
10. Pythagoras Theorem: In the case of a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides
11. Median: A line joining the mid-point of a side of a triangle to the opposite vertex is called a median. The point where the three medians of a triangle meet is called the centroid.
12. The centroid of a triangle divides each median in the ratio .
13. A point where the internal angle bisectors of a triangle intersect is called the incenter of the triangle.
14. Orthocenter of a triangle is the point of intersection of the altitudes of a triangle.
15. For a triangle, the circumcenter is equidistant from all the vertices.
Quadrilaterals
1. A rhombus is a parallelogram that has all the sides equal. In a rhombus, diagonals always bisect each other. Area
2. A quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel is called a parallelogram. Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. Area
3. A trapezium is a quadrilateral with only two sides parallel to each other. Area
Circles:
Area
Circumference
Area of a sector of a circle
i. The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord. The converse is also true.
ii. The perpendicular bisectors of two chords of a circle intersect at its centre.
iii. There can be one and only one circle passing through three or more non-collinear points
iv. If two circles intersect in two points then the line through the centres is the perpendicular bisector of the common chord.
v. If two chords of a circle are equal, then the centre of the circle lies on the angle bisector of the two chords.
vi. Equal chords of a circle or congruent circles are equidistant from the centre.
vii. Equidistant chords from the centre of a circle are equal to each other in terms of their length.
viii. In two concentric circles, the chord of the larger circle that is tangent to the smaller circle bisects at the point of contact.
Solid Figures:
4. Cube:
5. Cuboid:
6. Sphere:
7. Cylinder:
8. Cone:
9. Pyramid:
10. Prism:
11. Regular Tetrahedron:
