For a ___________________ internal energy of a system does not remain constant.
Any process in which the heat given out by the system is equal to the work done on the system.
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
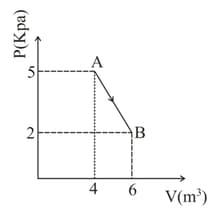
One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from to along a path as shown in figure. The change in internal energy of the gas during the transition is
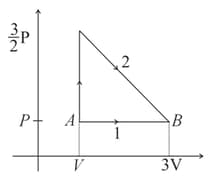
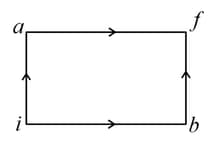
The diagram shown below indicates two paths along which a sample of gas can be taken from state to state . The energy equal to in the form of heat is required to be transferred if the Path- is chosen. How much energy in the form of heat should be transferred if Path- is chosen?
A gas undergoes a thermodynamic cycle as shown in pressure-volume diagram below. The heat transferred to the gas is and along path and respectively. The internal energy is changed by along path The work done by gas along path is
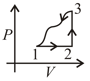
The equation of state of moles of a non-ideal gas can be approximated by the equation where, and, are constant characteristics of the gas. Which of the following can represent the equation of a quasi-static adiabatic for this gas (assume that, is the molar heat capacity at constant volume is independent of temperature)?
| Column – 1 | Column – 2 | Column – 3 |
| (I) | (i) Isothermal | (P) 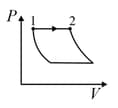 |
| (II) | (ii) Isochoric | (Q) 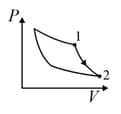 |
| (III) | (iii) Isobaric | (R) 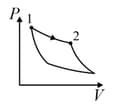 |
| (IV) | (iv) Adiabatic | (S) 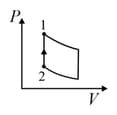 |
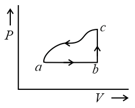
An ideal gas is made to undergo the cyclic process shown in the figure below.
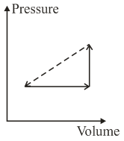
Let depict the work done, be the change in internal energy of the gas and be the heat added to the gas. Sign of each of these three quantities for the whole cycle will be ( refers to no change)
(I) and
(II) and
(III) and
(IV) and
Which of the above will lead to an increase in the internal energy of the system?
A given quantity of gas is taken from the state to the state reversibly by two paths, directly and as shown in the figure below:
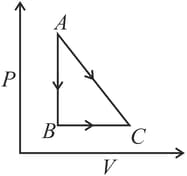
During the process , work done by the gas is and heat absorbed is . If during the process , the work done by the gas is , the heat absorbed is
When a system is taken from state to state along the path , it is found that and . Along the path , . along the path is,
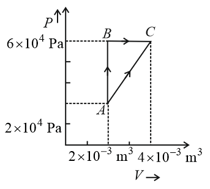
In process AB, of heat is added to the system and in process BC, of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be:

